As shown in the table in the Structure of Rate DM section, Rate DM is made up of a system access charge and a variable amount reflecting your energy consumption, divided into two tiers. The first tier (1st tier) is billed at a lower price than the second tier (2nd tier).
More kilowatthours at the lowest price
From 1978 to March 31, 2017, the 1st tier was set at 30 kWh a day, or 900 kWh a month. On April 1, 2017, it was increased from 30 to 33 kWh a day; on April 1, 2018, from 33 to 36 kWh a day; and on April 1, 2019, from 36 to 40 kWh a day. This is advantageous for consumers whose electricity consumption is relatively low, especially low-income households that use electricity for heating.
The 10 kWh a day that have been added to the 1st tier since April 1, 2017, translate into:
- Up to 300 kWh a month billed at a more advantageous rate
- Up to 35% in savings

Structure of Rate DM
- System access charge per day in the consumption period, times the multiplier: 46.154¢
- Price of energy for energy consumption up to the product of 40 kilowatthours (kWh), the number of days in the consumption period and the multiplier (1st tier): 6.905¢/kWh
- Price of energy for the remaining energy consumption (2nd tier): 10.652¢/kWh
- Charge for power demand exceeding the greater of 50 kilowatts (kW) or 4 kW times multiplier: $7.054/kW
Rates effective April 1, 2025. This table does not replace the Electricity Rates document in any way whatsoever.
Understanding rates
Rates generally have three main components that reflect the actual costs incurred by Hydro‑Québec to provide electrical service.
Electricity rates also include other components
More information
To find out more about Rate DM, consult Section 4 of Chapter 2 of the Electricity Rates [PDF 2.31 MB].
Other useful information
How to request electricity service
Bulk metering
Method of measuring energy consumed with a single meter instead of separate meters for an entire multiunit commercial or residential building. The building owner is responsible for dividing the costs between the occupants.
Separate metering
Method of measuring energy consumed with a separate meter for each residential or commercial unit in a building.
System access charge
A set amount, expressed in dollars per month or cents per day depending on the applicable rate, that the customer must pay for the electricity service.
Beginning April 1, 2019, the term fixed charge was replaced with system access charge.
Energy
Power used by electrical equipment over a given period of time. Expressed in kilowatthours (kWh), energy is calculated as power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), multiplied by the time during which the power is used, expressed in hours (h).
The formula for energy is as follows: energy (in kilowatthours) is equal to power (in kilowatts) multiplied by duration of use (in hours).
Energy (kWh) = power (kW) x time used (h).
Power
Total amount of electricity supplied at a given time. Expressed in kilowatts (kW), power is the combined effect of voltage, expressed in kilovolts (kV), and current, expressed in amperes (A).
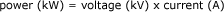
Winter period
Period from December 1 through March 31 of the next year, inclusive.
Summer period
Period from April 1 through November 30, inclusive.
Real power
Amount of electricity consumed in a useful manner to operate equipment, such as a motor or a heating or lighting system. Real power is expressed in kilowatts (kW).
Apparent power
Amount of electricity that Hydro-Québec supplies to a customer, expressed in kilovoltamperes (kVA). When it is used, apparent power breaks down into real power (kW), which runs devices, and reactive power (kVAR), which produces magnetic fields and which is not useful power for the customer.
Minimum billing demand (minimum demand)
The minimum amount of power that customers must pay for each consumption period, regardless of their electricity use. The threshold is set so that customers pay their share of the costs Hydro‑Québec incurs to meet their power needs at all times. The minimum billing demand is determined by the conditions of each rate, as indicated in the Electricity Rates.
- For all rates except Rate L, the minimum billing demand is automatically determined based on the previous winter’s maximum power demand.
- Rate L customers must set their own minimum billing demand, called “contract power,” based on their projected electricity use.
Maximum power demand
Maximum power measured during a consumption period. It is the higher of the following two values: real power in kilowatts (kW), or a percentage (90% for domestic rates and small- and medium-power rates, or 95% for large-power rates) of the apparent power in kilovoltamperes (kVA).
Rate
Electricity rate effective April 1, 2025.
Voltage
Difference in electrical level between two points, expressed in volts (V).
Low voltage: Voltage of 750 volts (V) or less.
Medium voltage: Voltage of more than 750 V, but less than 44 kilovolts (kV).
High voltage: Voltage of 44 kV or more.
Consumption period
Period during which electricity is delivered to the customer and which extends between the two dates used by Hydro‑Québec for calculation of the bill.
Power demand
Power a customer requires to meet energy needs at a given time. The higher the customer’s energy consumption at a given time, the higher the power demand.
Monthly periods
Period of 30 days, which may begin on any day of the month, established by Hydro‑Québec for billing purposes.
